Mydecine Innovations Group (MYCO.NE) announced they have signed a five-year research agreement with Johns Hopkins University (JHU) School of Medicine.
The research will be led by Dr. Matthew Johnson and the Behavioural Pharmacology Research Unit. Dr. Johnson is one of the world’s most published scientists on the human effects of psychedelics, and has conducted seminal research in the behavioral economics of drug use, addiction, and risk behavior. He has been working with psychedelics since 2004 and published psychedelic safety guidelines in 2008.
“We are excited to expand on the current work we are conducting with Dr. Matt Johnson and his team at JHU in regards to smoking cessation to include numerous other projects over the next five years. The researchers at JHU have proven their incredible depth of knowledge in the field,” stated Mydecine CEO Josh Bartch.
John Hopkins has the 7th highest ranked school of medicine for research, so working with them will be a good opportunity for Mydecine. John Hopkins conducts lab research as well as clinical trials. They have previously conducted research on 5-MeO-DMT, a psychedelic compound that is found in the venom of Bufo Alvarius toads. The study was successful, as 80% of the 362 people surveyed their anxiety and depression had improved after using DMT.
“The long-term potential of this research agreement is captivating for us here at Mydecine,” Chief Scientific Officer and Co-Founder of Mydecine, Rob Roscow, stated. “It demonstrates our commitment to advancing psychedelic medicine by exploring multiple molecules and medicines for a variety of indications.”
The research will include the treatment of addiction, as Dr. Johnson has researched this area before. Johnson has published 119 scientific manuscripts, including 47 manuscripts focused on psychedelics. In 2014, he published the first research on psychedelic treatment for tobacco addiction. That study, titled ‘Pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction’, has been cited nearly 500 times, and two out of three of Johnson’s most cited papers relate to tobacco consumption.
The pilot study found that 80% of smokers showed seven-day point prevalence abstinence at 6-month follow-up. For comparison, nicotine 2 mg chewing gum had an overall efficacy of 6% and really only had an effect in ‘high dependency’ smokers. This study, which was taken as evidence of the value of nicotine replacement therapies, found that “nicotine replacement therapy could enable about 15% of smokers who seek help in stopping smoking to give up the habit.” When you compare nicotine therapy and psychedelics, it’s not even close.
“Despite the recent attention to opiate and dependance on other illicit substances, we sometimes forget about the incredible burden that nicotine dependence has on our societies,” stated Dr. Rakesh Jetly, Chief Medical Officer, Mydecine. “According to the CDC, cigarette smoking is the leading cause of preventable disease and death in the United States, killing more than 480,000 Americans each year. Despite all the public education and dire warnings, cigarette smoking remains one of the most difficult addiction to treat and contributes to more deaths than all the other substances combined, making research like this vital.”
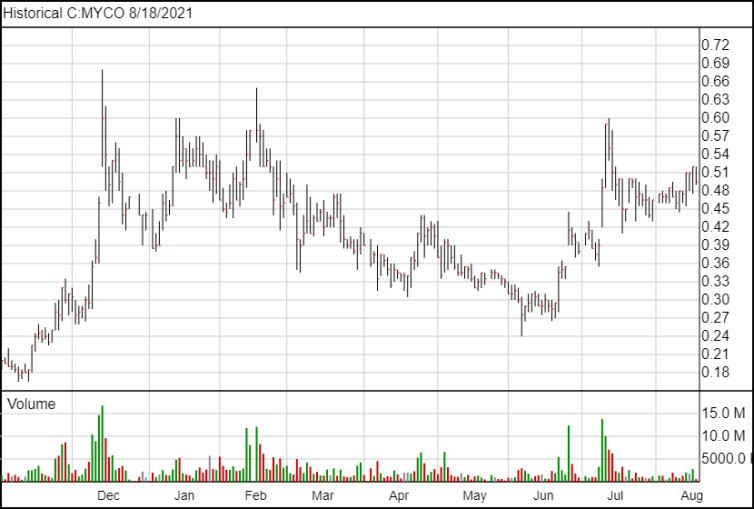
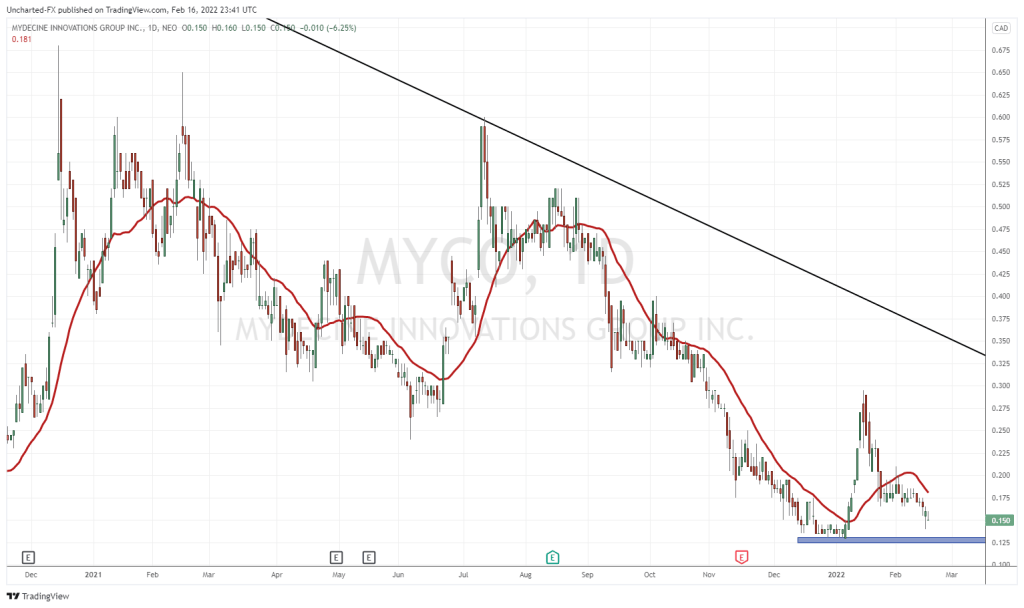
Following the news, MYCO shares are down two and a half cents and are currently trading at $0.495.